All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
What Are The Benefits Of Double Glazed Windows? in Woodvale WA
Glazing merely indicates the windows in your house, including both openable and set windows, as well as doors with glass and skylights. Glazing actually just indicates the glass part, however it is generally utilized to describe all aspects of an assembly consisting of glass, films, frames and home furnishings. Taking note of all of these elements will help you to accomplish efficient passive style.
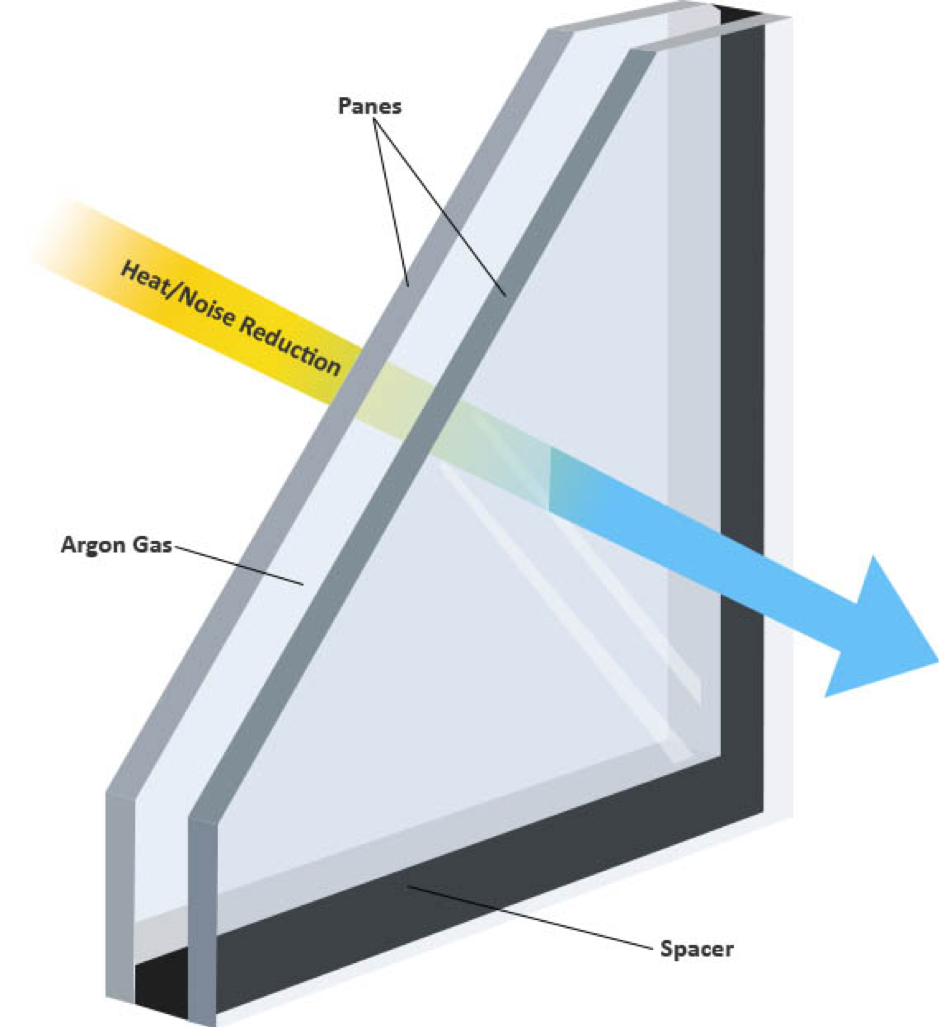
Energy-efficient glazing makes your house more comfortable and dramatically decreases your energy expenses. Improper or inadequately created glazing can be a major source of undesirable heat gain in summertime and considerable heat loss and condensation in winter. As much as 87% of a house's heating energy can be gotten and as much as 40% lost through windows.
Double Glazed Windows in Currambine WA
Glazing is a considerable financial investment in the quality of your home. The expense of glazing and the expense of heating and cooling your home are closely related. An initial financial investment in energy-efficient windows, skylights and doors can greatly reduce your annual heating and cooling expense. Energy-efficient glazing also minimizes the peak heating and cooling load, which can reduce the needed size of an air-conditioning system by 30%, causing further cost savings.

This tool compares window selections to a base level aluminium window with 3mm clear glass. Understanding some of the essential properties of glass will assist you to select the finest glazing for your home. Key homes of glass Source: Adjusted from the Australian Window Association The quantity of light that passes through the glazing is referred to as noticeable light transmittance (VLT) or noticeable transmittance (VT).
Plastic Window Frames - Best Plastic Double Glazed ... in Mount Lawley Perth
This may lead you to turn on lights, which will result in higher energy costs. Conduction is how readily a material performs heat. This is understood as the U worth. The U worth for windows (expressed as Uw), describes the conduction of the entire window (glass and frame together). The lower the U worth, the greater a window's resistance to heat flow and the better its insulating value.
If your house has 70m2 of glazing with aluminium frames and clear glass with a U worth of 6. 2W/m2 C, on a winter's night when it is 15C colder outside compared with inside your home, the heat loss through the windows would be: 6. 2 15 70 = 6510W That is comparable to the overall heat output of a large room gas heating system or a 6.
What Are Double Glazed Windows? - Build in Parkwood WA

If you select a window with half the U value (3. 1W/m2 C) (for instance, double glazing with an argon-filled gap and less-conductive frames), you can cut in half the heat loss: 3. 1 15 70 = 3255W The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) for windows (expressed as SHGCw) determines how easily heat from direct sunshine flows through an entire window (glass and frame together).
The lower a window's SHGC, the less solar heat it sends to the house interior. The actual SHGC for windows is impacted by the angle that solar radiation strikes the glass.
Why Should You Have Double-glazed Windows This Summer? in Maylands WA
When the sun is perpendicular (at 90) to the glass, it has an angle of incidence of 0 and the window will experience the optimum possible solar heat gain. The SHGC declared by glazing manufacturers is always determined as having a 0 angle of occurrence. As the angle increases, more solar radiation is shown, and less is transferred.
Latest Posts
Fitting A Cabin In Your Garden? Get Double Glazing Fitted Too in Forrestdale WA
Why Is Double Glazing So Important In Winter? in Highgate Perth
Best Glass For Double Glazing in Gwelup Perth